Motheye structures for Solar Photovoltaics
Optics • Photovoltaics • 2014 • Nano structuresMasters thesis
Solar Panels are affected by several losses. In one of my previous projects, I worked to improve the efficiency of solar panels by aligning the panel to the angle of maximum intensity. Assuming that the panel is aligned to match the angle at which intensity, the efficiency is still low. One of the major losses is the reflection loss at the top layer due to the big difference in the refractive indices between air and the topmost layer of Solar PV. Nearly 55% of the light is reflected. Though anti-reflection coatings are available, they work for specific wavelengths only, and their efficiency is low too.
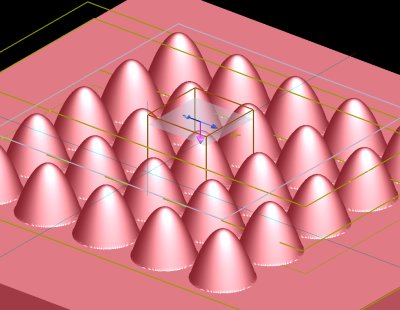
I took this problem for my master's thesis. I'm a big fan of bio-mimicry. I often find ideas when I'm on a hike or away from the city and immersed in nature. After some research, I found that moth's eyes have a special anti-reflection coating that helps the moth to hide its presence from the predator. I built upon some existing research and redesigned my solar PV. I did several simulations and optimisations to find the best arrangement to minimise loss over a wide range of wavelengths. My design has less than 1% reflection loss over a wide range of wavelengths.
Comparison of structure and response to incident light
My design efficiently traps the light inside the layers of a solar panel and minmises the relection loss to
less than 1 % as compared to nearly 30-50% loss
in traditional designs. In the simulation below at a the timeshot where light is incident and a at a later
timestep after reflection appears, it is apparent that my
design is able to trap the solar radiation.
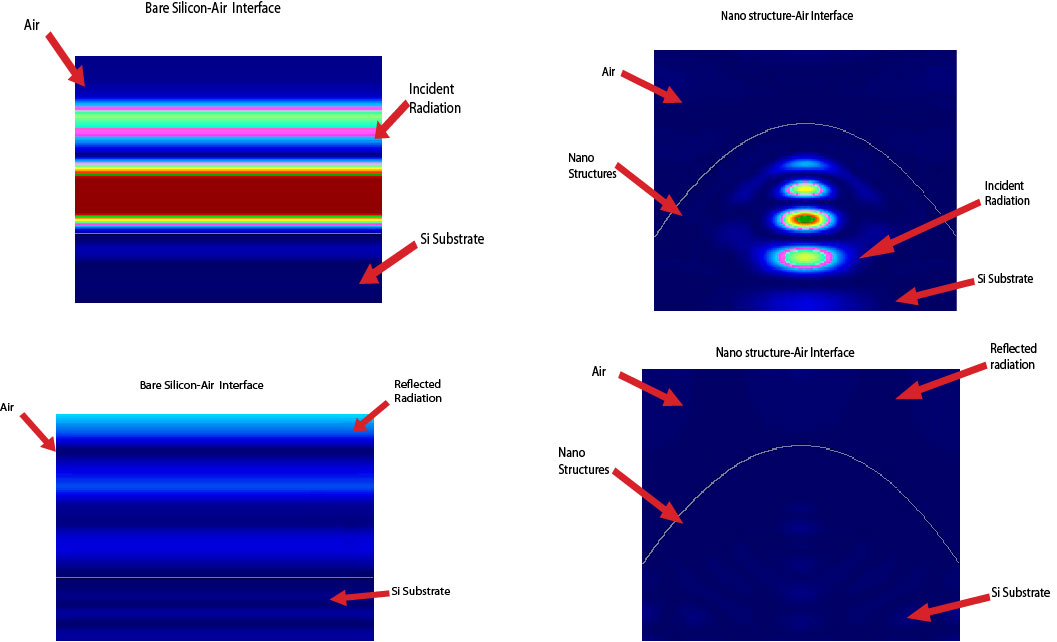
Some of the key results :
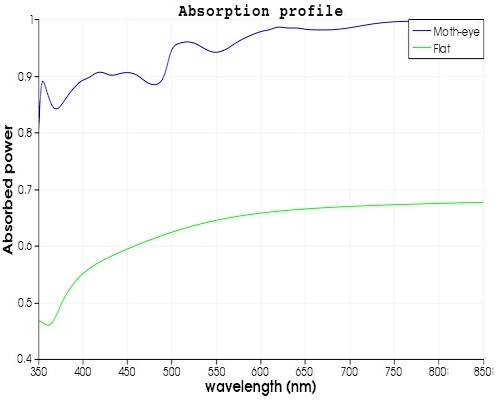
Comparison of performance of the my design when with the regular solar panel without nano structures
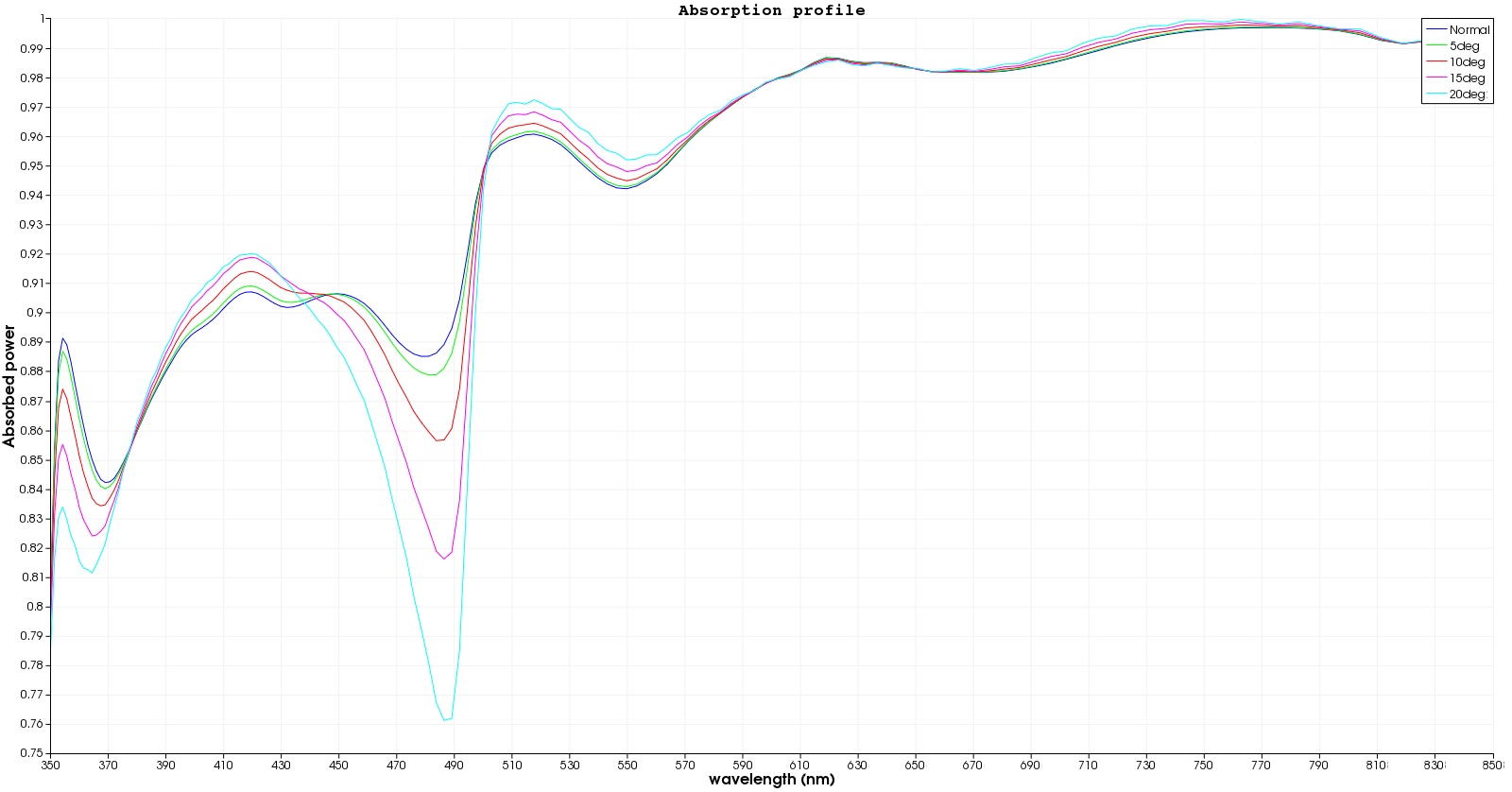
Performance of the optimised nanostructure design over diferrent angle in incidence